e-Invoicing
On-Cloud Deployment of the E-Invoicing Solution
Cloud deployment is a model in which IT infrastructure and applications are hosted and managed on remote servers owned and operated by a cloud service provider (CSP). Businesses can access their applications and data through the internet, often using web-based interfaces or APIs.
SaaS represents applications hosted and managed in the cloud by a CSP, accessible through web browsers or APIs. SaaS removes the need for businesses to install or manage software on their own devices or servers.
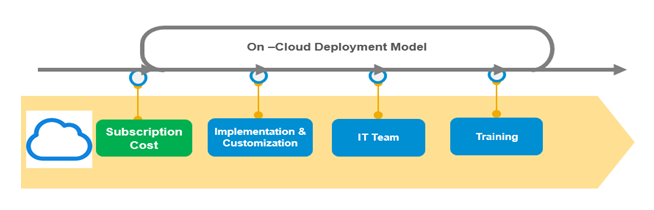
Wizard’s also offers E-Invoicing Solution/system as a SaaS based model. Wizard offers Single Tenant and multi-Tenant E-Invoice application. Wizard’s E-Invoicing solution is developed in AWS Cloud Environment.
1. Public cloud
Public Cloud deployment is one of the popular SaaS deployment models that leverage the infrastructure and resources offered by a third-party cloud service provider.
In this model, the SaaS application is hosted and operated in the public cloud, accessible to multiple organizations and users over the Internet.
Multi-Tenant: Multi-tenant architecture is a cloud environment where multiple customers share software instances and the supporting infrastructure.
Security is paramount in multi-tenant architectures, as customers share the same infrastructure and resources. Here are several key security measures used by Wizard’s E-Invoicing Solution:
- Tenant-specific data, configurations, and user accounts
- Role-based access control (RBAC) and permissions
- Encrypting databases, backups, and communication between different system components
- Authentication and authorization
- Firewalls and network segmentation
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
- Certifications like SOC 2, ISO 27001,
- Tenant-level customization to meet specific needs without affecting other tenants
2. Private Cloud
A private cloud is a specialized cloud computing architecture for a single organization. It is intended to give exclusive access to computing resources, storage, and networking infrastructure, ensuring greater data security and control.
Single Tenant: A dedicated instance of an application that is managed by the vendor. A dedicated software application, server, and database for every client. Premium price and the need to invest in maintenance, setup, hosting, and infrastructure updates.
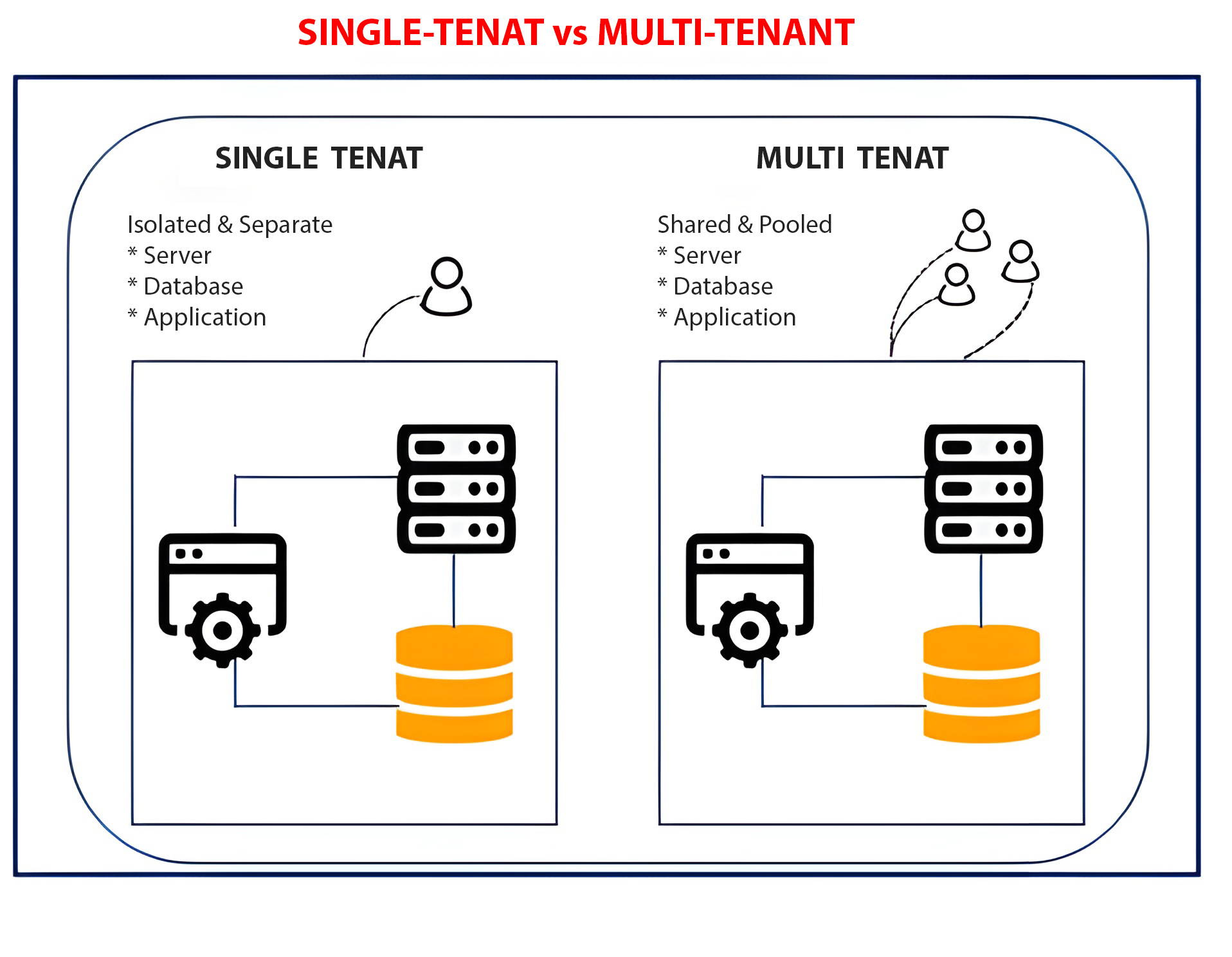
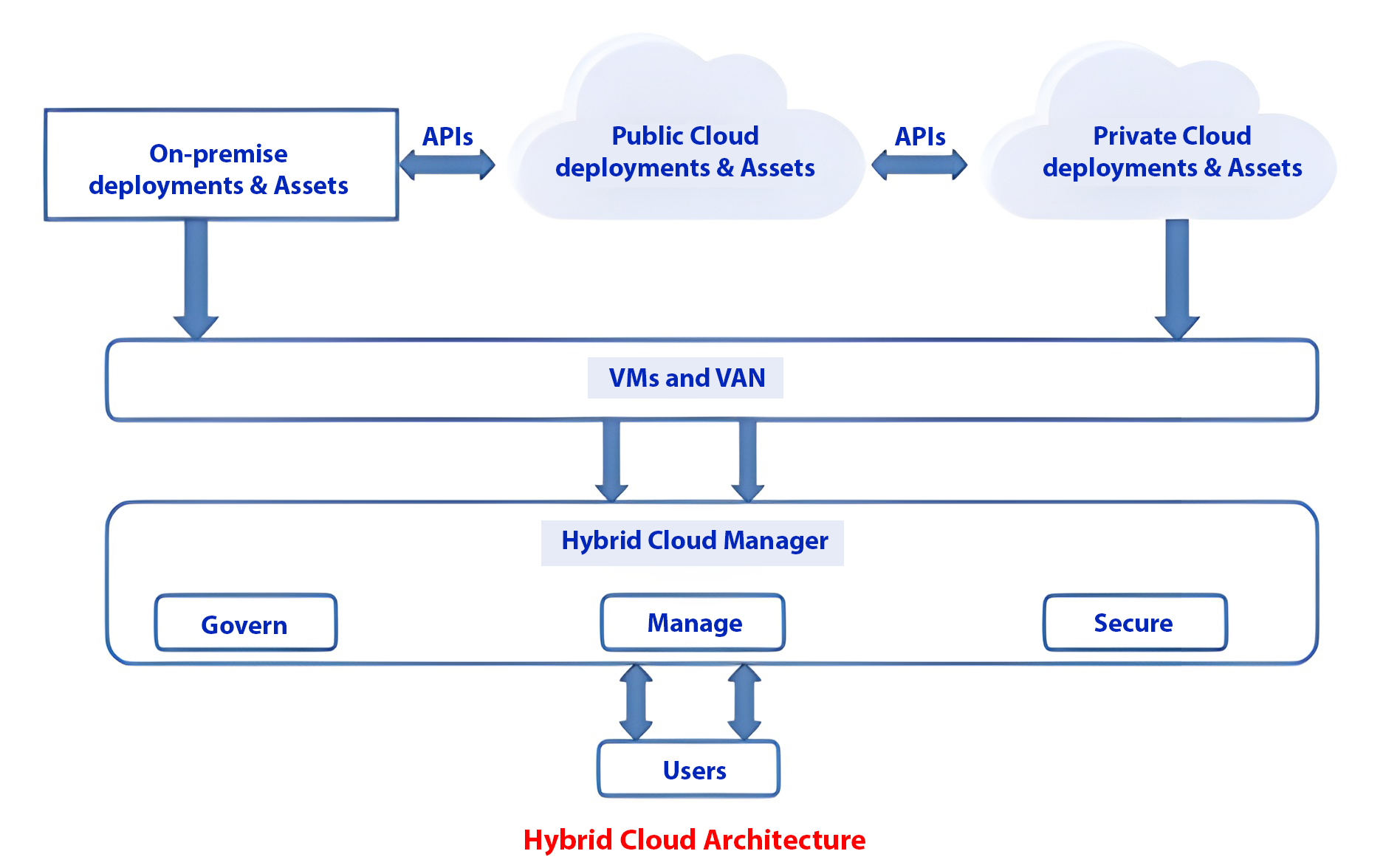
Hybrid Model:
A hybrid cloud model combines private and public cloud resources, allowing organizations to leverage both benefits. The idea is to create an integrated infrastructure that provides the best of both worlds.
Advantages:
- Ability to leverage the benefits of both private and public clouds, such as digital sovereignty, compliance, cyber security, disaster recovery, and scalability.
- Optimization of costs by using public clouds for non-critical workloads and private clouds for critical workloads.
- Agility in managing growing amounts of data and quickly responding to changing needs and opportunities via cloud migration.
- Enabling different use cases like secure collaboration.






